Advanced configuration
In this page, we will cover some configurations which are specific to AWS Lambda Authorizer. Detailed documentation of all Gate configuration options is available in the Configuration page.
Per lambda / URL configuration
You can modify how Gate works for each Lambda instance/URL by defining per-URL configuration.
You can do so by using a pattern and enabling/disabling plugins or setting specific plugin parameters for each URL.
An example pattern for Lambda could be cz1ljn5dv7.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/stage_name/hello or */stage_name/hello.
You should not include the protocol (https://) in the pattern.
You can learn more about URL configuration in the URL configuration page.
Passing headers
This section will demonstrate how to pass headers from a Lambda Authorizer to the protected service.
AWS Lambda Authorizers cannot modify request or response headers automatically.
Request headers
Gate has access to all headers from the incoming request. Some plugins may modify those headers (this will be described in the plugin documentation). In this scenario, you must explicitly configure Gate to pass headers to the protected service.
Gate will pass all request headers in context, so you can use $context to access request headers.
Header names are converted to lowercase, and all non-alphanumeric characters are replaced with underscore (_).
For example, the Users Mirroring plugin will add a SlashID-PersonID header if a new person was created.
The created person ID will be available in the authorizer context: $context.authorizer.requestHeaders.slashid_personid.
You can check available headers by using Test functionality in Lambda Authorizer configuration.
Navigate to the Test tab in Lambda configuration and paste the following JSON to the Event JSON field:
{
"version": "2.0",
"type": "REQUEST",
"routeArn": "arn:aws:execute-api:us-east-1:123456:i6x4fg8hfc/test/GET/echo",
"routeKey": "GET /echo",
"rawPath": "/test/echo",
"rawQueryString": "",
"cookies": null,
"headers": {
"accept": "*/*",
"accept-encoding": "gzip, deflate",
"authorization": "Bearer topsecret",
"cache-control": "no-cache, no-store, must-revalidate,max-age=0",
"content-length": "0",
"host": "i6x4fg8hfc.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com",
"pragma": "no-cache",
"x-forwarded-for": "127.0.0.1",
"x-forwarded-port": "443",
"x-forwarded-proto": "https"
},
"queryStringParameters": null,
"requestContext": {
"routeKey": "GET /echo",
"accountId": "123456789",
"stage": "test",
"requestId": "MX_NWiSDoAMEaRg=",
"apiId": "i6x4fg8hfc",
"domainName": "i6x4fg8hfc.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com",
"domainPrefix": "i6x4fg8hfc",
"time": "06/Oct/2023:10:19:13 +0000",
"timeEpoch": 1696587553924,
"http": {
"method": "GET",
"path": "/test/echo",
"protocol": "HTTP/1.1",
"sourceIp": "127.0.0.1",
"userAgent": "curl"
}
}
}
Now click the Test button. If everything works correctly, you should see the banner:
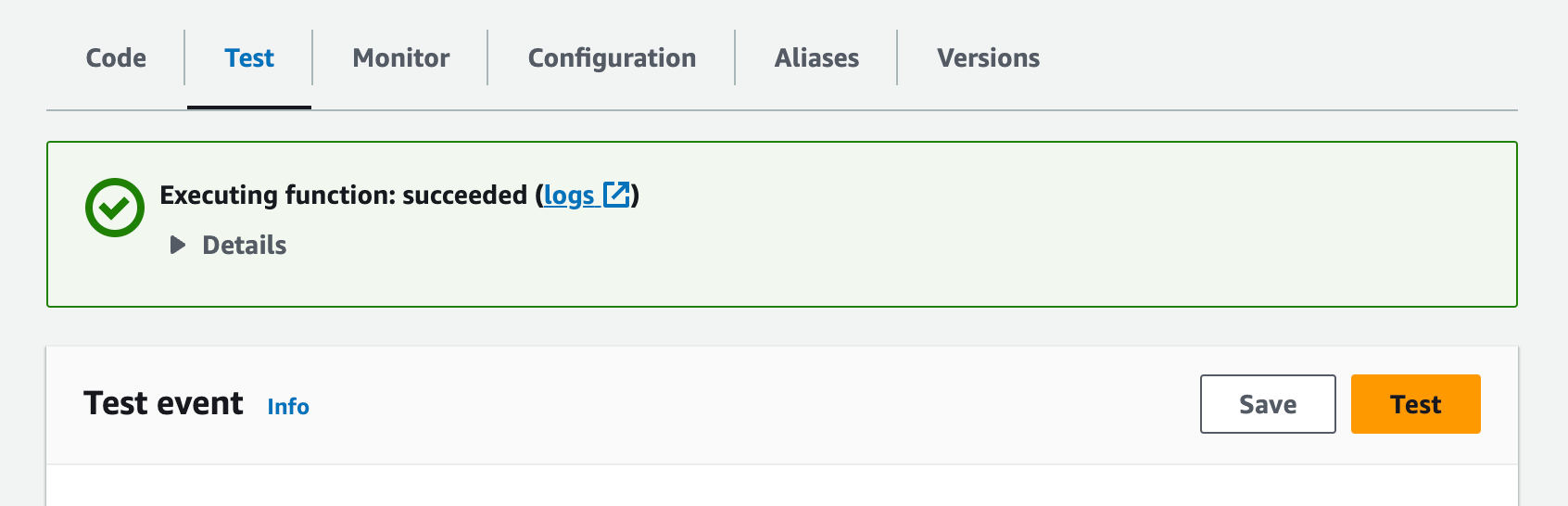
When you extend the Details section, you should see logs and output from Gate Lambda.
- Terraform
- AWS UI
To map request headers, use the request_parameters configuration in the aws_apigatewayv2_integration resource.
resource "aws_apigatewayv2_integration" "echo_lambda" {
api_id = aws_apigatewayv2_api.lambda_gateway.id
integration_uri = aws_lambda_function.echo.invoke_arn
integration_type = "AWS_PROXY"
integration_method = "POST"
request_parameters = {
"append:header.SlashID-PersonID" = "$context.authorizer.requestHeaders.slashid_personid"
}
}
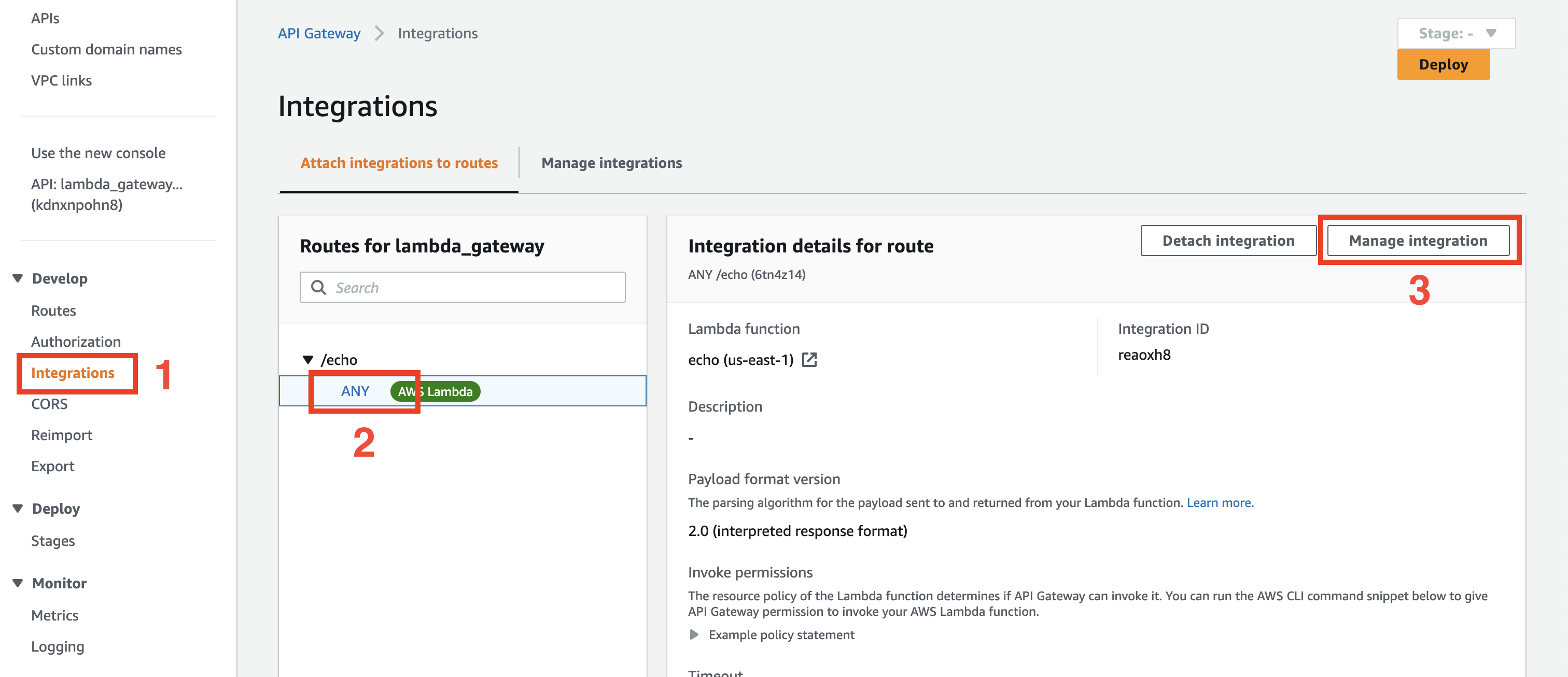
To map request headers, open API Gateway configuration
and choose the lambda_gateway API. Then choose Integrations, your echo Lambda integration and click Manage integration.
Now you can set:
- Mapping type:
All incomming requests - Parameter to modify:
header.SlashID-PersonID - Modification type:
append - Value:
$context.authorizer.requestHeaders.slashid_personid
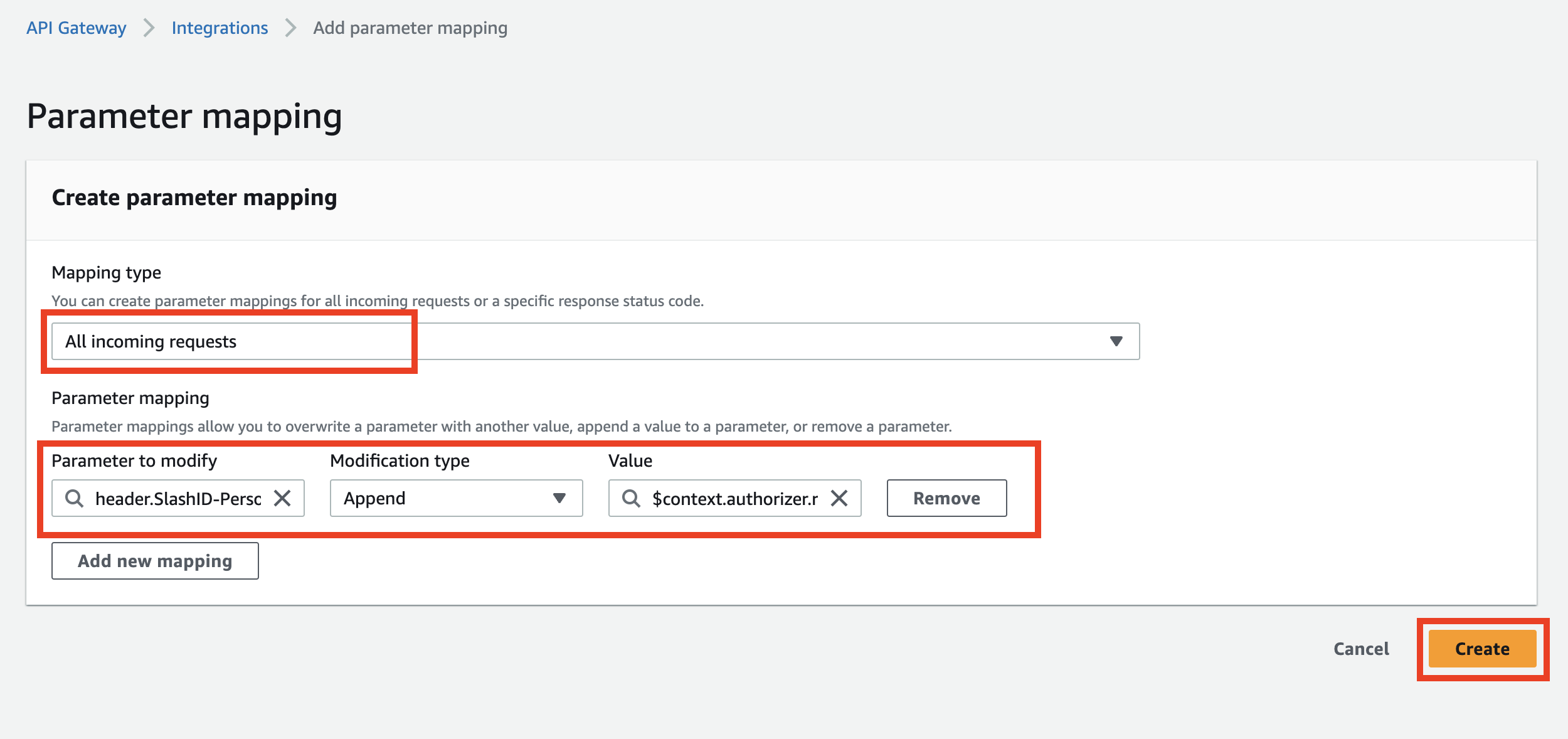
After adding this mapping, your Lambda will start to receive the SlashID-PersonID request header.
The full reference for the request_parameters syntax is available in the AWS documentation and Terraform documentation.
Response headers
Some plugins may add headers to the response. In this scenario, you need to configure Gate to add those headers to the response explicitly.
Gate will pass all response headers in context, so you can use $context to access request headers.
Header names are converted to lowercase, and all non-alphanumeric characters are replaced with underscore (_).
For example, the Rate Limiting plugin will add a RateLimit-Remaining header to the response.
It will be available in the Authorizer context: $context.authorizer.responseHeaders.ratelimit_remaining.
- Terraform
- AWS UI
To map request headers, use the response_parameters configuration in the aws_apigatewayv2_integration resource.
resource "aws_apigatewayv2_integration" "echo_lambda" {
api_id = aws_apigatewayv2_api.lambda_gateway.id
integration_uri = aws_lambda_function.echo.invoke_arn
integration_type = "AWS_PROXY"
integration_method = "POST"
dynamic "response_parameters" {
for_each = [200, 201, 202, 204, 301, 302, 303, 400, 401, 403, 404, 405, 408, 409, 410, 500, 501, 502, 503]
content {
status_code = response_parameters.value
mappings = {
"append:header.RateLimit-Remaining" = "$context.authorizer.requestHeaders.ratelimit_remaining"
}
}
}
}
Unfortunately, AWS requires explicit configuration for each status code. We can overcome this problem with dynamic blocks.
We hardcoded the most popular status codes, but you can create the mapping for all available status codes by using
for_each = range(200, 599)
Please remember that this will create a very large configuration, so it is not recommended.
To map request headers, open API Gateway configuration
and choose the lambda_gateway API. Then choose Integrations, your echo Lambda integration and click Manage integration.


Now you can set:
- Mapping type:
Response (based on status code) - Response status code: status code for which you want to add a header (unfortunately, you need to specify all status codes manually)
- Parameter to modify:
header.RateLimit-Remaining - Modification type:
append - Value:
$context.authorizer.requestHeaders.ratelimit_remaining
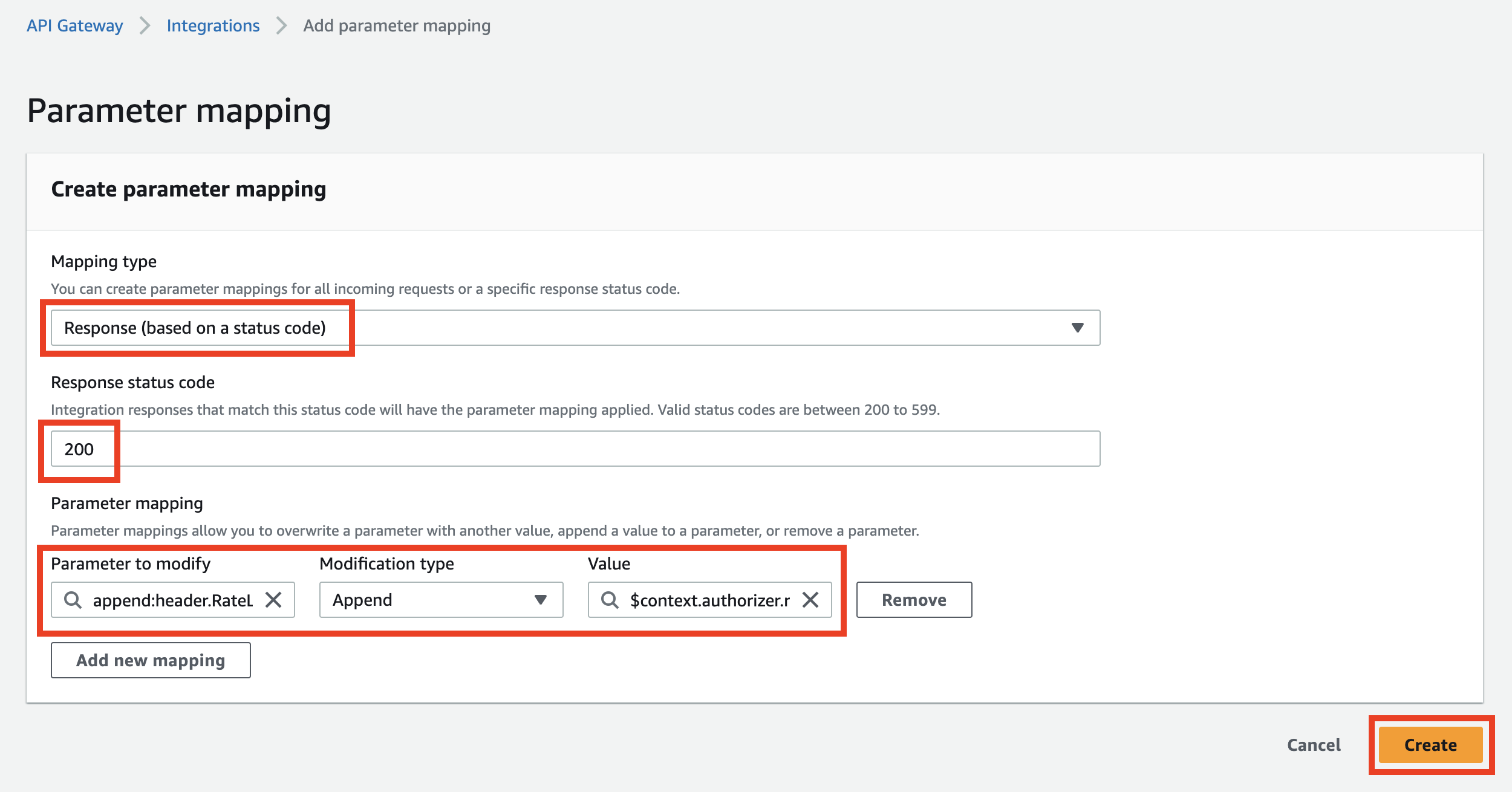
After adding this mapping, your Lambda will start to return the RateLimit-Remaining response header.
The full reference of supported request_parameters syntax is available in the AWS documentation and Terraform documentation.
Further reading
You can check Use Cases page for more use cases.